Most Sample Code from "Java How to Program, Fifth Edition" from Deitel and Deitel.
From: http://www2.cs.uregina.ca/~nova/Java_Study/Examples5/
And see the index here: http://www2.cs.uregina.ca/~nova/Java_Study/
Three main ways of handling events
example: Application_E1.java
indications of this method:
public class myclass extends JFrame implements ActionListener
exit.addActionListener(this);
public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent actionEvent)
// as a member function of the primary class
example: Application_E2.java
indications of this method:
MyHandler handler = new MyHandler();
exit.addActionListener(handler)
private class MyHandler implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent actionEvent)
example: Application_E3.java
indications of this method:
exit.addActionListener(
new ActionListener() { //anonymous inner class
public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent event)
{
System.exit(0);
}
}
);
The following is meant to summarize what happens when you click a button:
JButton (click) --------->ActionEvent Object------>Processed by
OR JTextField (enter) Created ActionListener's
actionPerformed
function
JCheckBox Processed by
JRadioButton --------------->ItemEvent Object-------->ItemListener's
OR JComboBox Created itemStateChanged
selection function
JCheckBox Buttons
Example code: CheckBoxTest.java
creating and adding checkboxes is simple:
JCheckBox bold;
bold = new JCheckBox ("Bold");
container.add (bold);
Which of three above methods are we using to implement event handling?
method 2
*Notice that there is an inner class that implements ItemListener and defines the itemStateChanged function.
JRadioButton
Example code: RadioButtonTest.java
creating and adding radiobuttons:
JRadioButton plainButton, boldButton, italicButton, boldItalicButton;
ButtonGroup radio Group;
...
plainButton = new JRadioButton ("Plain", true);
container.add (plainButton);
boldButton = new JRadioButton( "Bold", false );
container.add( boldButton );
italicButton = new JRadioButton( "Italic", false );
container.add( italicButton );
boldItalicButton = new JRadioButton( "Bold/Italic", false );
container.add( boldItalicButton );
// create logical relationship between JRadioButtons
radioGroup = new ButtonGroup();
radioGroup.add( plainButton );
radioGroup.add( boldButton );
radioGroup.add( italicButton );
radioGroup.add( boldItalicButton );
Why do we need a Radio group?
because only one radio button is selected at a time.
Which method of event handling?
method 2 (have an inner class)
Notice in the code like the following
plainButton.addItemListener(new RadioButtonHandler(plainFont);
we are calling the constructor for the RadioButtonHandler
and sending it a font argument. The four calls like this
create four different
ItemListeners (one for each button). Each ItemListener has the
private font variable set appropriately for the corresponding button
JComboBox
Example code: ComboBoxTest.java
bug1.gif
bug2.gif
travelbug.gif
buganim.gif
creating and adding ComboBoxes:
JComboBox imagesComboBox;
String names[] = { "bug1.gif", "bug2.gif", "travelbug.gif",
"buganim.gif" };
imagesComboBox = new JComboBox( names );
imagesComboBox.setMaximumRowCount( 3 );
container.add(imagesComboBox);
Which method of event handling?
method 3
JPasswordField
Example code: TextFieldTest.java
creating and adding PasswordFields:
JPasswordField passwordField;
passwordField= new JPasswordField("Hidden text");
container.add(passwordField);
Which method of event handling?
method 2
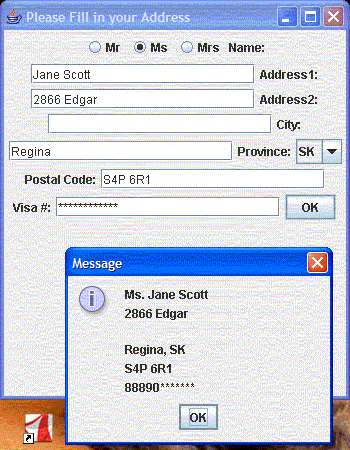
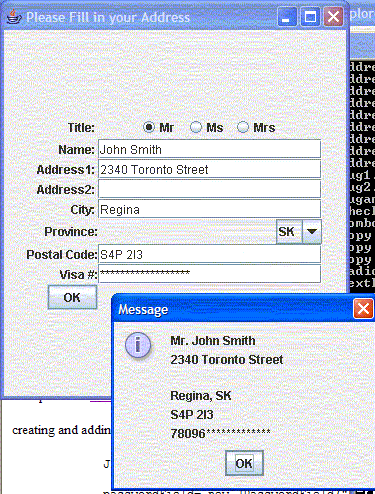
Exercise
Create a GUI interface that looks like this. When you click on "OK" a message box pops up.